
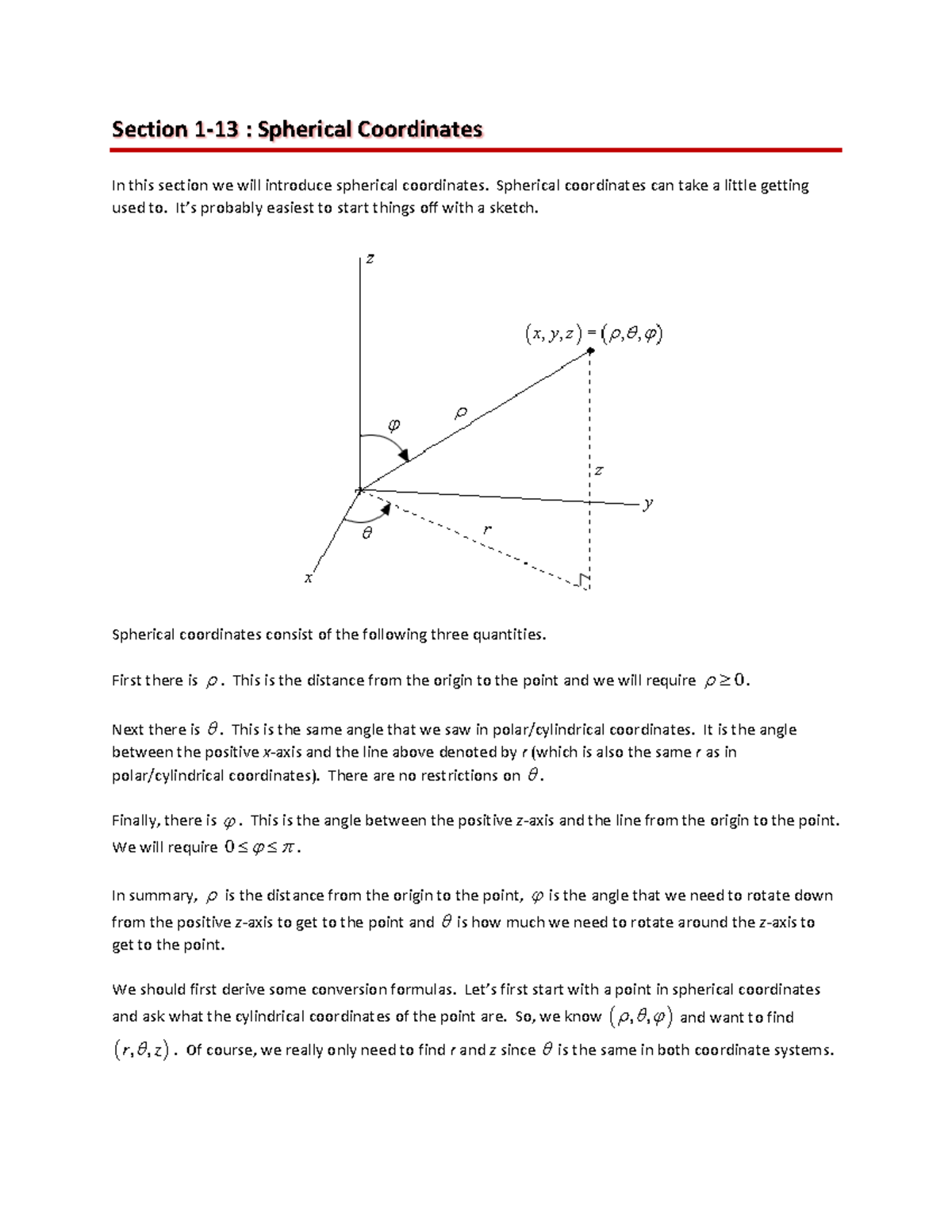
However, the azimuth φ is often restricted to the interval (−180°, +180°], or (− π, + π ] in radians, instead of [0, 360°). If it is necessary to define a unique set of spherical coordinates for each point, one must restrict their ranges.
#CALC 3 SPHERICAL COORDS FINS PHI ISO#
This article will use the ISO convention frequently encountered in physics: ( r, θ, φ ). The use of symbols and the order of the coordinates differs among sources and disciplines. The polar angle is often replaced by the elevation angle measured from the reference plane towards the positive Z axis the depression angle is the negative of the elevation angle. The polar angle may be called colatitude, zenith angle, normal angle, or inclination angle.

The radial distance is also called the radius or radial coordinate. When radius is fixed, the two angular coordinates make a coordinate system on the sphere sometimes called spherical polar coordinates. In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a point is specified by three numbers: the radial distance of that point from a fixed origin its polar angle measured from a fixed polar axis or zenith direction and the azimuthal angle of its orthogonal projection on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the fixed axis, measured from another fixed reference direction on that plane. In this image, r equals 4/6, θ equals 90°, and φ equals 30°. A globe showing the radial distance, polar angle and azimuthal angle of a point P with respect to a unit sphere, in the mathematics convention. As in physics, ρ ( rho) is often used instead of r, to avoid confusion with the value r in cylindrical and 2D polar coordinates. The meanings of θ and φ have been swapped compared to the physics convention. Spherical coordinates ( r, θ, φ) as often used in mathematics: radial distance r, azimuthal angle θ, and polar angle φ. This is the convention followed in this article. 3-dimensional coordinate system Spherical coordinates ( r, θ, φ) as commonly used in physics ( ISO 80000-2:2019 convention): radial distance r ( slant distance to origin), polar angle θ ( theta) (angle with respect to positive polar axis), and azimuthal angle φ ( phi) (angle of rotation from the initial meridian plane).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
